Calcium Carbonate Mineral Formation, Dissolution, Structures, & Geological Significance
Calcium carbonate minerals buffer the ocean's pH, provide protection to animals with CaCO3 skeletons or shells, provide homes to organisms that live in coral

Biomineralization: Integrating mechanism and evolutionary history

Crystallization of Calcium Carbonate: Modeling Thermodynamic Equilibrium, Pathway, Nucleation, Growth, Agglomeration, and Dissolution Kinetics with the Presence of Mg2+, Ba2+, and Sr2+

Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate

How to Balance Sodium carbonate + Calcium chloride

Biomineralization (Pt 3): Do Bacteria Solve The Dolomite Problem?

The Side Effects of Calcium Carbonate You Need to Know

Process-Specific Effects of Sulfate on CaCO3 Formation in Environmentally Relevant Systems
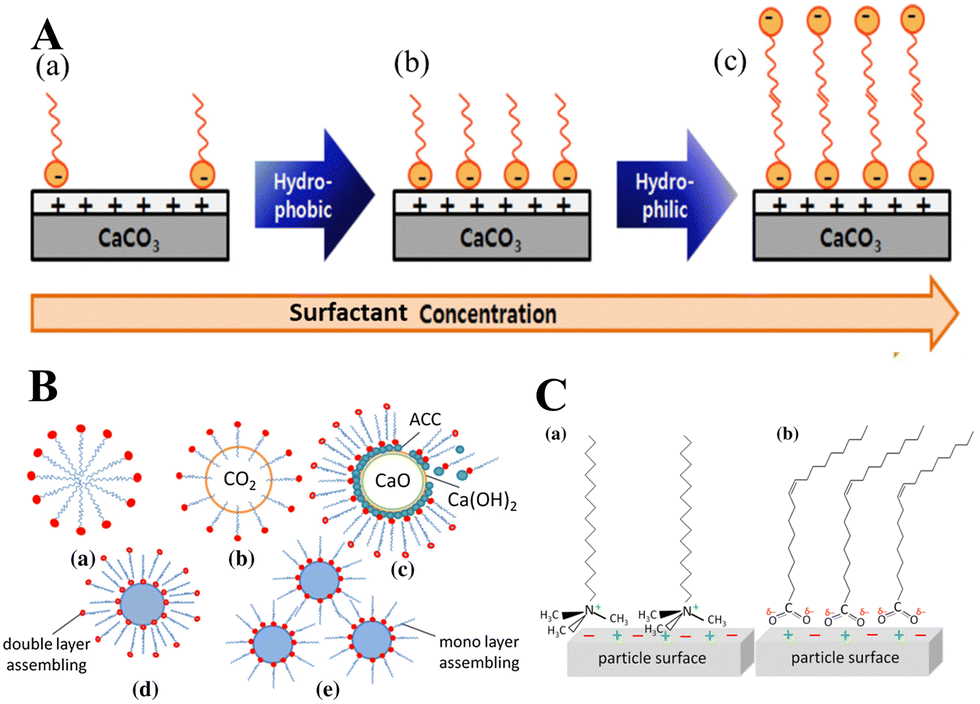
Calcium carbonate: controlled synthesis, surface functionalization, and nanostructured materials - Chemical Society Reviews (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1CS00519G

Carbonate Mineralization - a SOLID Method for CO2 Capture

Science at Home: Vinegar and Calcium Carbonate

Is CaCO3 (Calcium carbonate ) an Electrolyte or Non-Electrolyte?
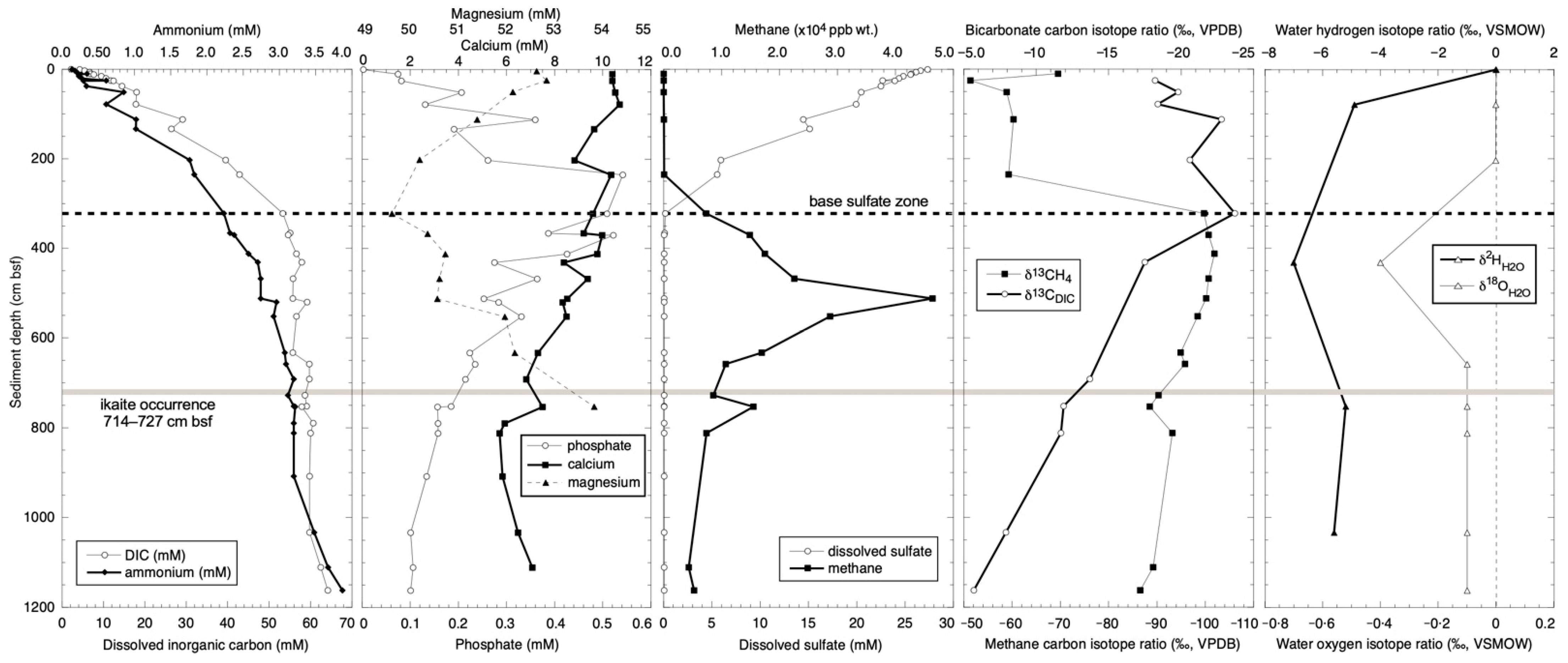
Minerals, Free Full-Text
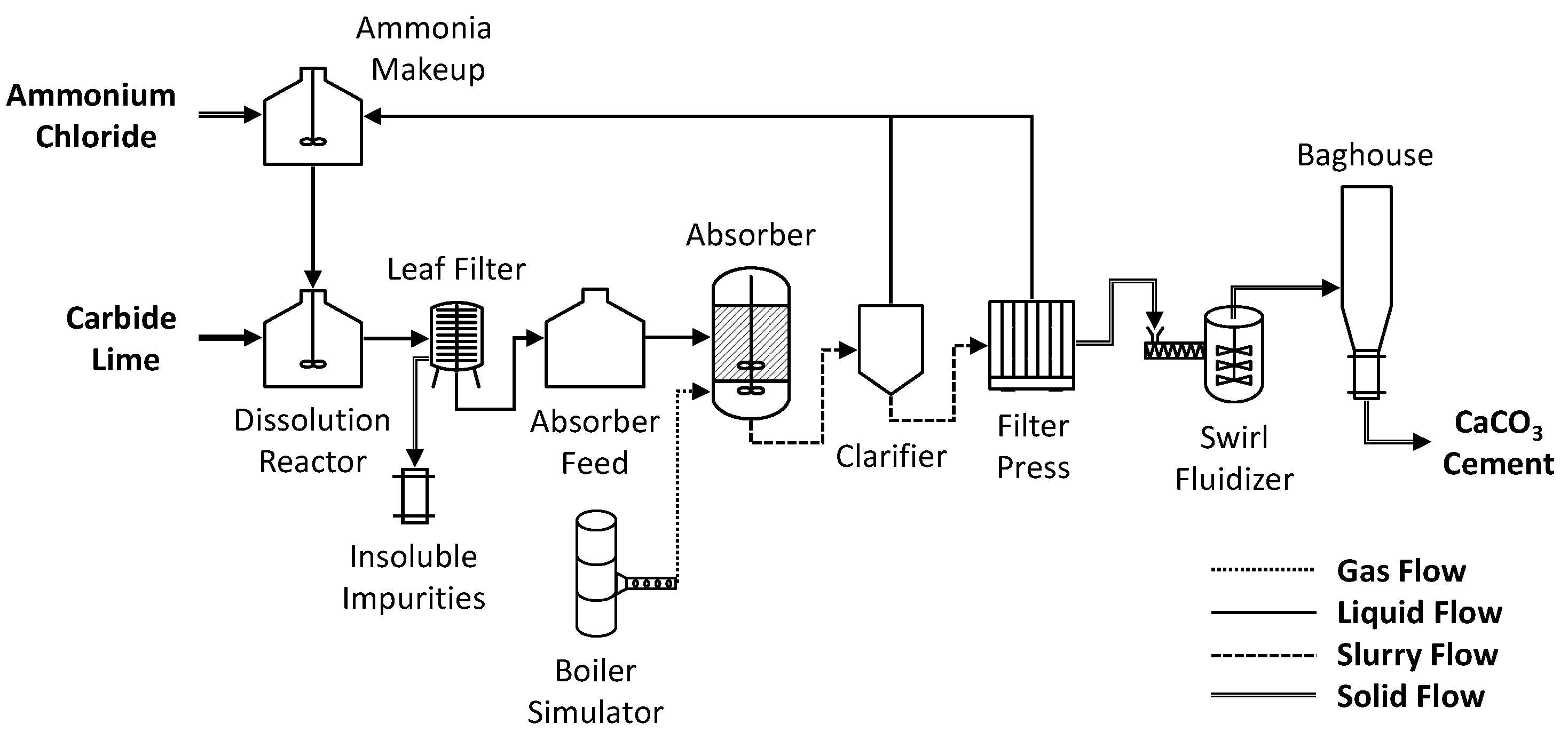
Materials, Free Full-Text

How to Write the Formula for Calcium Carbonate

How to draw the Lewis Dot Structure for Calcium Carbonate









