The Science Behind UV-C Energy: What Is It? - UV Resources
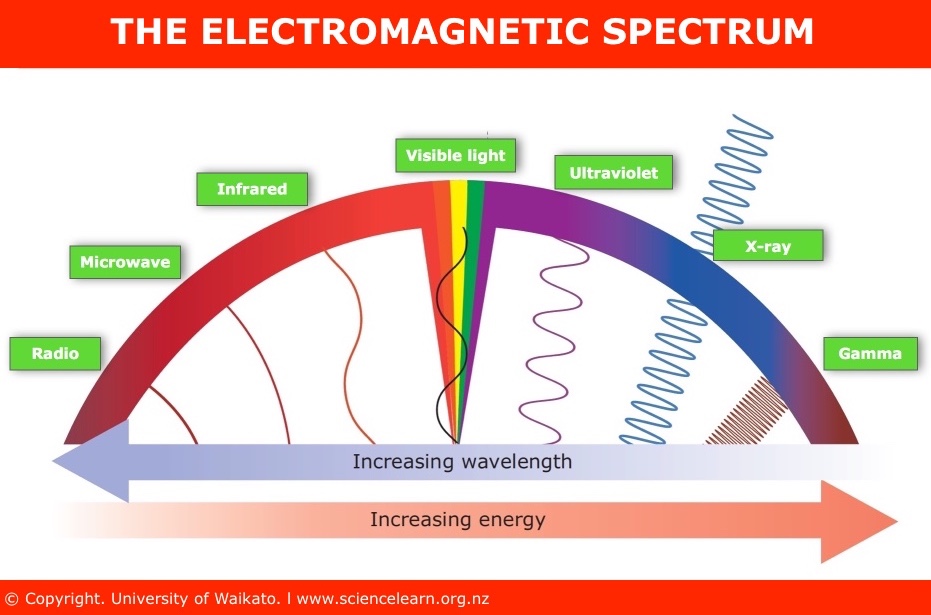
UV light comprises a segment of the electromagnetic spectrum between 400 and 100 nm, corresponding to photon energies from 3 to 124 eV. The UV segment has four sections, labeled UV-A (400 to 315 nm), UV-B (315 to 280 nm), very high energy and destructive UV-C (280 to 200 nm), and vacuum UV. Most of us are familiar with the harmful effects of UV energy transmitted by sunlight in the UV-A and UV-B wavelengths, giving rise to UV “sunburn” inhibitors, or blocking agents, which are found in glasses and lotions. We are also familiar with products engineered to withstand the effects of UV radiation, such as plastics, paints, and rubbers. However, unlike the UV-A and UV-B wavelengths, the UV-C band has more than twice the electron volt energy (eV) as UV-A, and it is well absorbed (not reflected) by organic substances, adding to its destructiveness.

The Science Behind UV-C Energy: What Is It? - UV Resources

What is the Difference Between UV-A and UV-C?

Unwanted Indoor Air Quality Effects from Using Ultraviolet C Lamps for Disinfection

Facts About HVAC UV Light Air Quality Benefits

Techno-economic evaluation of UV light technologies in water remediation - ScienceDirect
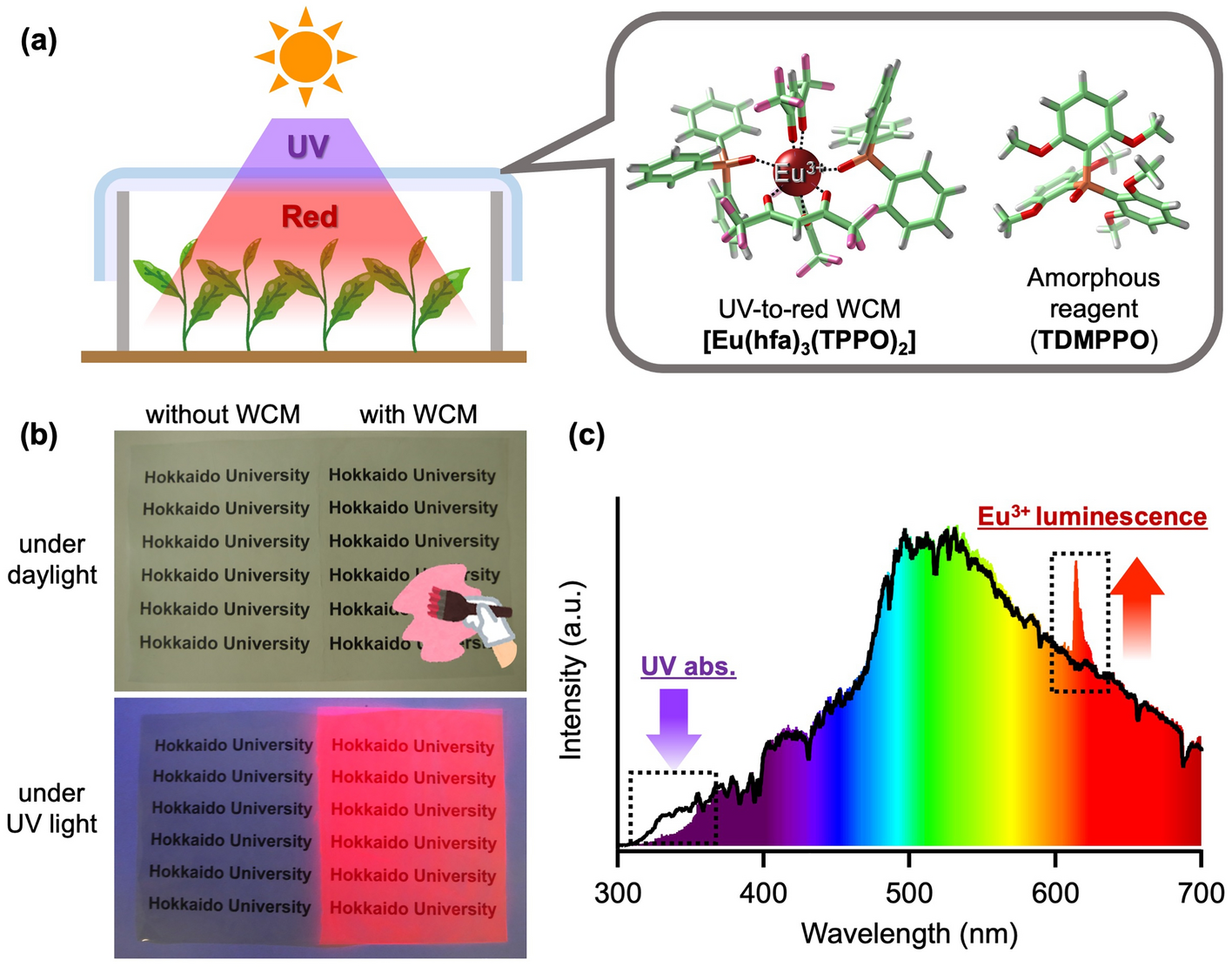
Plant growth acceleration using a transparent Eu3+-painted UV-to-red conversion film
What Is Germicidal Ultraviolet-C (UVC) light?
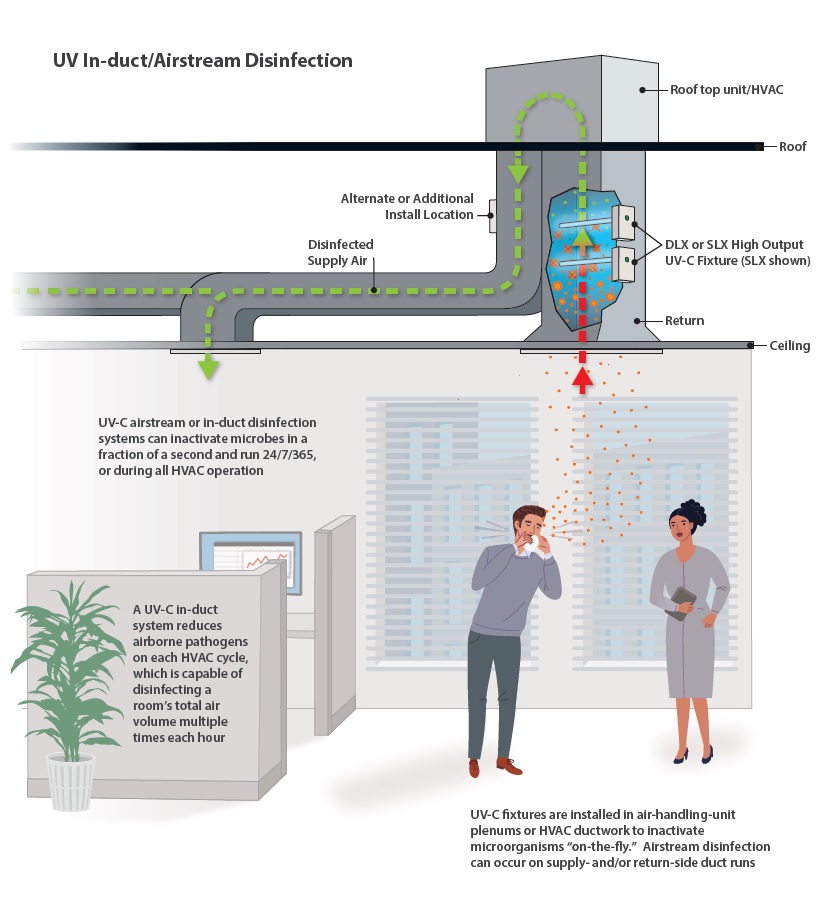
What Facility Managers Need to Know about Germicidal UV-C
What is UV? — Science Learning Hub
UV-Light Air Purifier: What Is It & How Does It Work? - Molekule
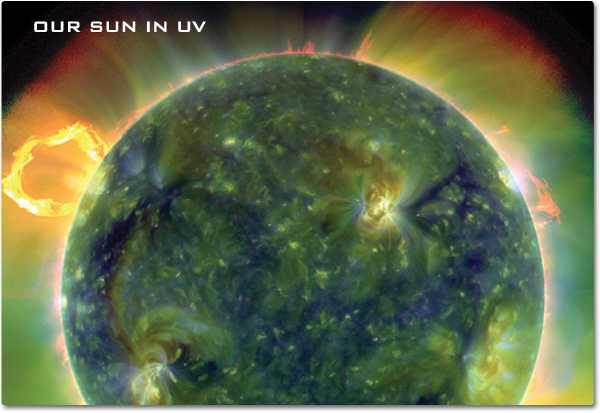
Ultraviolet Waves - NASA Science

What is the Difference Between UV-A and UV-C?
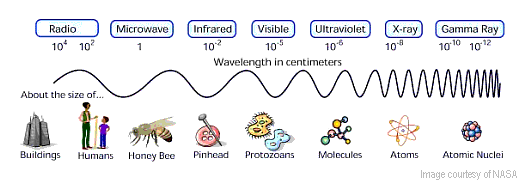
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
The Science Behind UV-C Energy: What Is It? - UV Resources

How Does UVC Technology Work?