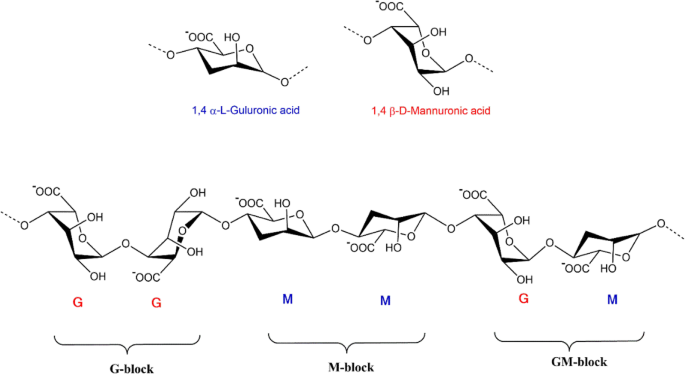
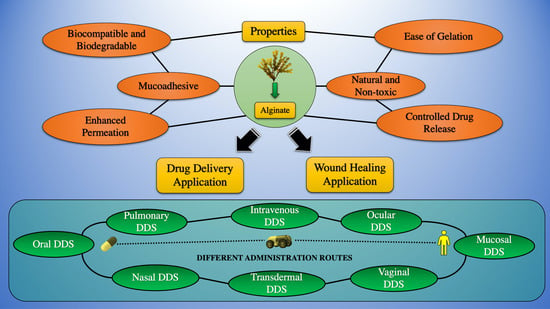
Alginate-based hydrogels as drug delivery vehicles in cancer
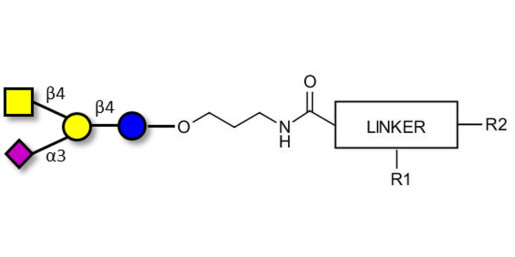
Hydrogels are a three-dimensional and crosslinked network of hydrophilic polymers. They can absorb a large amount of water or biological fluids, which leads to their swelling while maintaining their 3D structure without dissolving (Zhu and Marchant, Expert Rev Med Devices 8:607–626, 2011). Among the numerous polymers which have been utilized for the preparation of the hydrogels, polysaccharides have gained more attention in the area of pharmaceutics; Sodium alginate is a non-toxic, biocompatible, and biodegradable polysaccharide with several unique physicochemical properties for which has used as delivery vehicles for drugs (Kumar Giri et al., Curr Drug Deliv 9:539–555, 2012). Owing to their high-water content and resembling the natural soft tissue, hydrogels were studied a lot as a scaffold. The formation of hydrogels can occur by interactions of the anionic alginates with multivalent inorganic cations through a typical ionotropic gelation method. However, those applications require the control of some properties such as mechanical stiffness, swelling, degradation, cell attachment, and binding or release of bioactive molecules by using the chemical or physical modifications of the alginate hydrogel. In the current review, an overview of alginate hydrogels and their properties will be presented as well as the methods of producing alginate hydrogels. In the next section of the present review paper, the application of the alginate hydrogels will be defined as drug delivery vehicles for chemotherapeutic agents. The recent advances in the application of the alginate-based hydrogels will be describe later as a wound dressing and bioink in 3D bioprinting.

Sodium alginate based drug delivery in management of breast cancer - ScienceDirect

Synthesis and Evaluation of Alginate-Based Nanogels as Sustained Drug Carriers for Caffeine
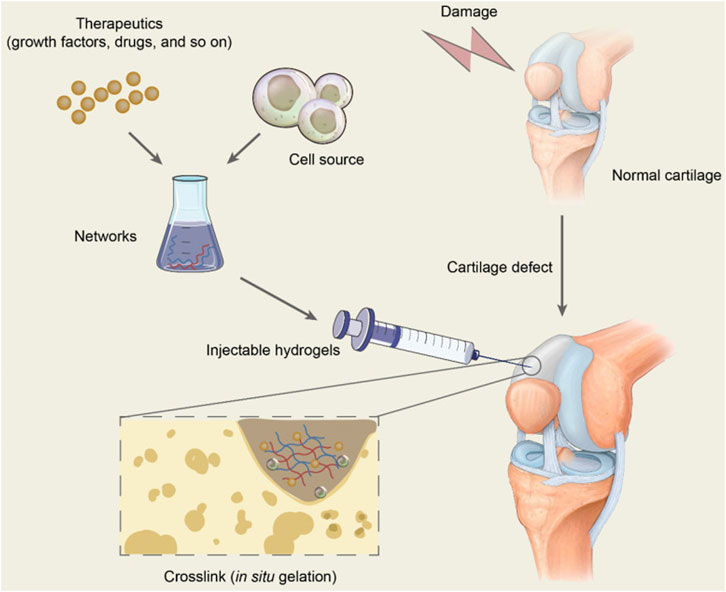
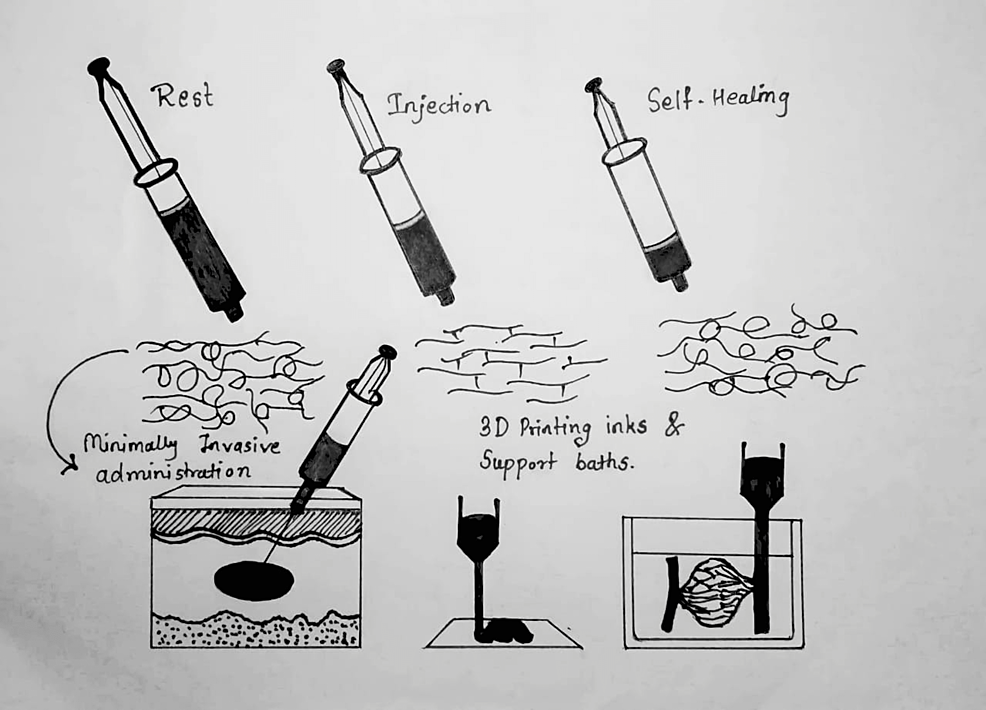
Frontiers Advanced injectable hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering

Polymers, Free Full-Text
Sources of Extraction and Properties of Alginate
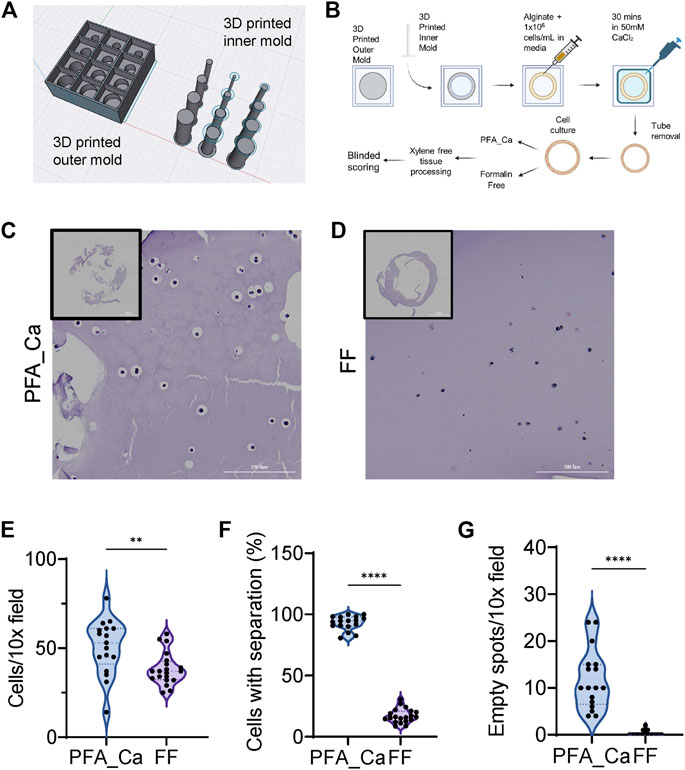
Frontiers Formalin-free fixation and xylene-free tissue processing preserves cell-hydrogel interactions for histological evaluation of 3D calcium alginate tissue engineered constructs
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Cureus, Injectable and Self-Invigorating Hydrogel Applications in Dentistry and Periodontal Regeneration: A Literature Review

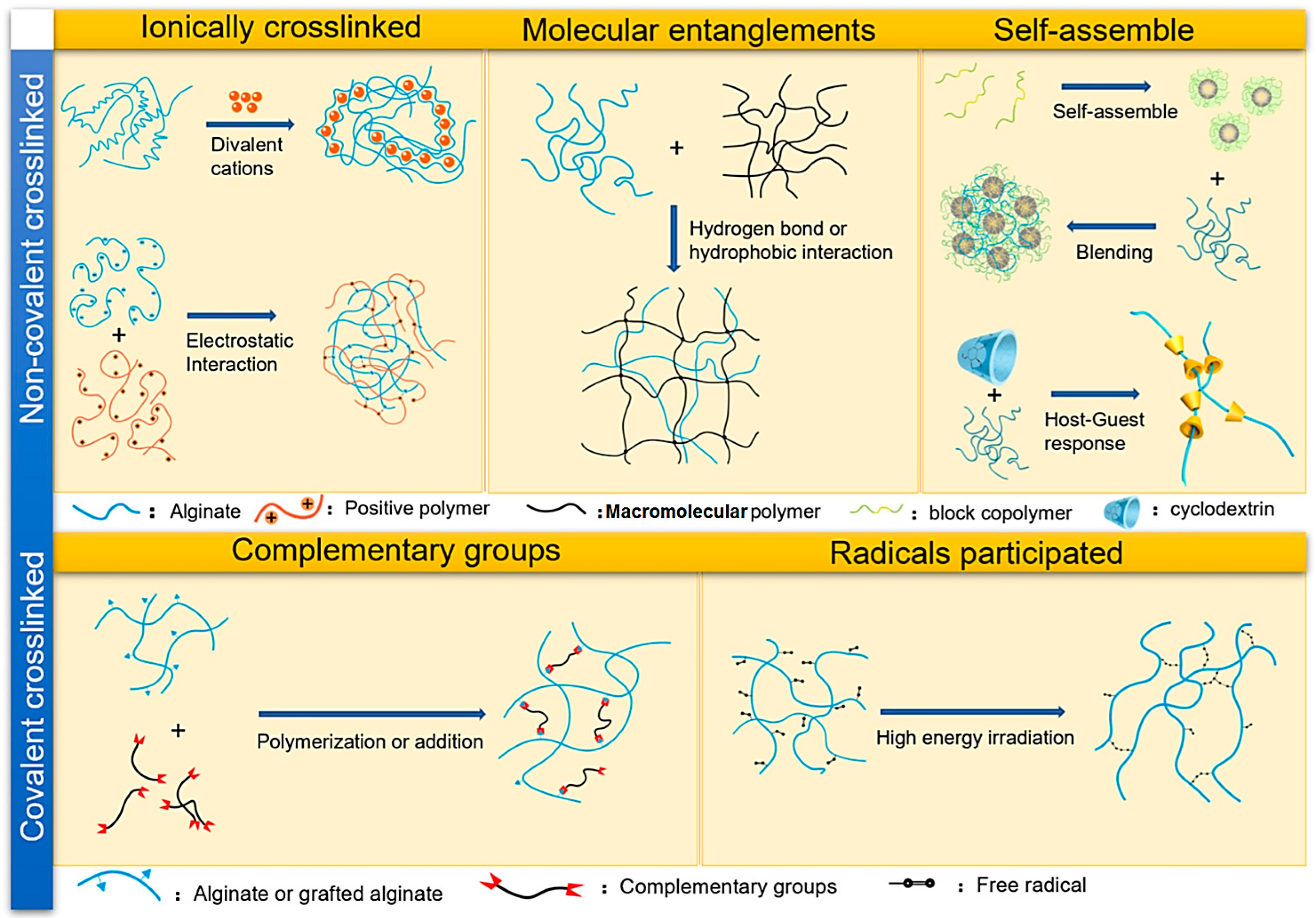
Alginate Metal Complexes and Their Application

Alginate Based Micro Particulate Systems for Drug Delivery
Marine Drugs, Free Full-Text

Sodium alginate: the wonder polymer for controlled drug delivery

Alginate-based hydrogels for cancer therapy and research - ScienceDirect

Alginate-based Hydrogels As Drug Delivery Vehicles In, 45% OFF
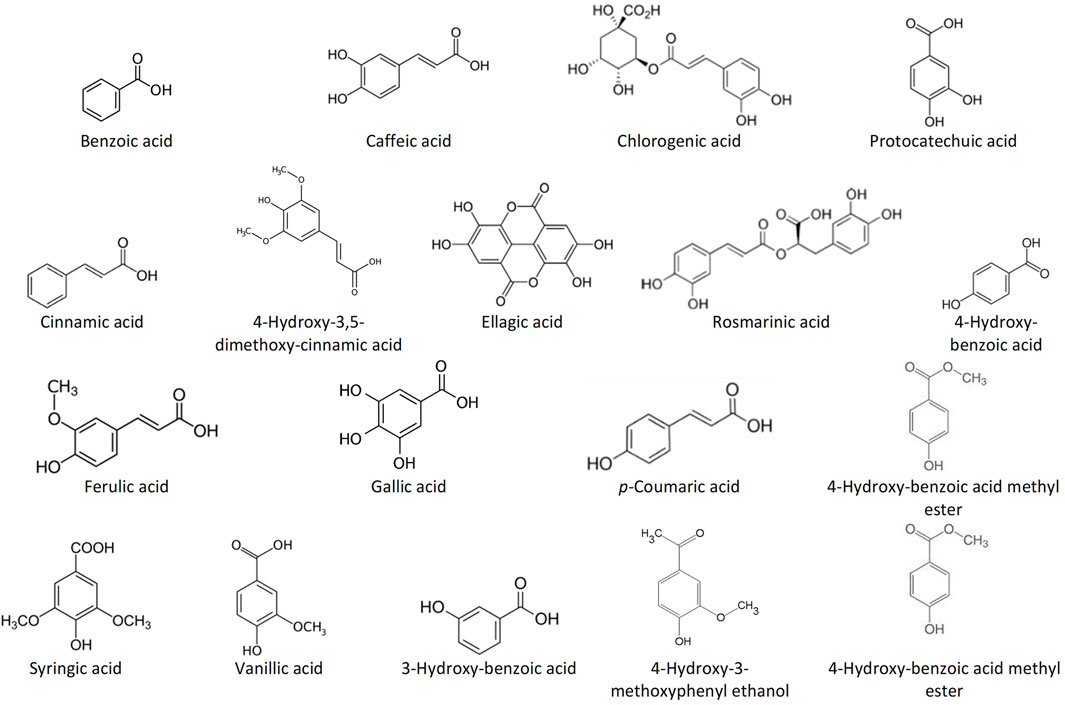
Frontiers Applications of Alginate-Based Nanomaterials in Enhancing the Therapeutic Effects of Bee Products



/product/12/1416101/1.jpg?0299)



